Exploring Different Types of Marketing: From Guerrilla to Buzz

Marketing is no longer just about traditional TV ads or billboards. In today’s dynamic digital world, brands are constantly finding new and creative ways to connect with their audiences. From unconventional campaigns to real-time engagement, different marketing approaches can help businesses stand out and make a lasting impact.
Let’s explore some of the most popular and innovative types of marketing you should know.
1. Guerrilla Marketing

What it is: Guerrilla marketing is an unconventional, low-cost strategy that aims to grab attention through surprise, creativity, or shock value. It relies on bold, unexpected campaigns that make people stop and talk about the brand.
Example: A flash mob in a public square promoting a new product, or a cleverly placed street art ad that catches people off-guard.
Why it works: It creates memorable experiences and often generates word-of-mouth at a fraction of the cost of traditional advertising.
2. Moment Marketing

What it is: Moment marketing is all about brands responding quickly to trending events, viral moments, or cultural conversations with relevant content.
Example: A food brand tweeting a witty response during a popular sports match or creating a meme around a trending celebrity moment.
Why it works: It makes brands look relatable, agile, and in tune with their audience’s conversations.
3. Buzz Marketing

What it is: Buzz marketing focuses on creating excitement and anticipation around a product or campaign so that people start talking about it.
Example: A movie studio releasing mysterious teaser trailers or a brand launching a limited-edition product with hype-driven promotions.
Why it works: It taps into curiosity and FOMO (fear of missing out), encouraging people to share and discuss the brand organically.
4. Influencer Marketing
What it is: Collaborating with social media influencers or thought leaders to promote your product or service.
Example: A beauty brand partnering with a popular YouTuber or Instagram creator to showcase their new product line.
Why it works: Audiences trust influencers they follow, and recommendations feel more authentic than traditional ads.
5. Experiential Marketing
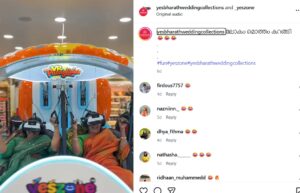
What it is: Also called engagement marketing, it focuses on creating immersive, hands-on brand experiences that let customers interact directly.
Example: A pop-up shop where customers can try products in fun, interactive ways, or a virtual reality demo of a new service.
Why it works: It builds emotional connections and makes the brand experience unforgettable.
6. Content Marketing

What it is: Creating and sharing valuable, relevant content (blogs, videos, podcasts, infographics) to attract and engage a target audience.
Example: A fitness brand running a YouTube channel with workout tutorials and nutrition tips.
Why it works: It positions the brand as a helpful authority and nurtures long-term relationships with customers.
7. Viral Marketing

What it is: Crafting campaigns designed to spread rapidly online through social shares. Viral content is often funny, emotional, or surprising.
Example: A quirky ad that becomes a trending TikTok challenge.
Why it works: It reaches huge audiences quickly and often at minimal cost if executed well.
8. Cause Marketing
What it is: 
Example: A clothing company donating a portion of proceeds to sustainability projects.
Why it works: It builds goodwill, enhances brand image, and resonates with socially conscious consumers.
9. Relationship Marketing

What it is: Focused on building strong, long-term customer relationships rather than one-time sales.
Example: Loyalty programs, personalized emails, or exceptional customer support.
Why it works: Retaining customers is more cost-effective than acquiring new ones, and loyal customers often become brand advocates.
10. Word-of-Mouth Marketing

What it is: Encouraging customers to share their positive experiences and recommend the brand to others.
Example: Referral programs that reward customers for bringing in friends.
Why it works: People trust recommendations from peers more than advertisements.
